Sunday, March 9, 2014
Self Reflection Chapter 25
This was a very interesting chapter. Western expansion and European imperialism have been mentioned in books I've read or movies I've watched, and we touched on how imperialism affected China and Japan last year in US History, but until we covered this chapter I've never had a solid understanding of imperialism, and British involvement in Egypt and India. It's nice to finally have a good understanding of the period. It's also helpful in understanding why imperialism is such a dirty word today. When you hear criticisms of US intervention in foreign countries as being imperialistic, it automatically registers as undesirable, but you don't truly understand how awful it is for a nation to be imperialistic until you've learned about some of the ghastly motivations and effects of European imperialism.
Spotlight on the Suez Canal

The Suez Canal is a man-made waterway in Egypt that connects the Mediterranean and Red seas. It was installed by the British, under the Suez Canal Company, and today is owned by the Suez Canal Authority, which in turn is owned by the Egyptian government. It is one of the most important waterways in the world, and is used extensively. It is the fastest way to cross from the Atlantic Ocean to the Indian Ocean, and thus is one of the world's most used shipping lanes.
Uprising in Syria
In March of 2011, protests erupted in Damascus, the capital of Syria. The protests were led by Syrians who opposed the regime of President Assad, and they demanded the release of political prisoners. Assad released some prisoners, but the unrest in Damascus didn't completely settle, and Assad turned to other tactics in an attempt to end the uprising, sending in tanks and troops. During this time, the opposition formed the Free Syrian Army, and organized the Syrian National Council. Fighting continued, and in August of 2012 the UN formally asked Assad to resign, and president Obama warned against the use of chemical weapons. Later in that year, the different factions of Syrian opposition formed the National Coalition for Syrian Revolutionary and Opposition Forces, which was then recognized by several countries, including the US, as the legitimate representative of the Syrian people. Early in 2013 Assad's warplanes bombed a rebel-controlled city, and the US and Britain pledged non-military aid to the Syrian opposition. Soon afterwards, reports emerged of chemical weapon use, and the US and Britain demanded investigations. In the fall of 2013, UN investigators concluded that chemical weapons were used, but did not allocate blame. Soon afterward, the US and Russia negotiated an agreement that Syria's chemical weapons would be destroyed. Unrest in Syria is still ongoing.
The Sepoy Mutiny
India was the jewel of the British Empire, and its most prized colony. In 1857, all independent states in India had been conquered, and India was governed primarily by the British East India Company. The British army in India contained Sepoys, Indian soldiers. In 1857, the Sepoys revolted. The insurrection erupted when the Sepoys, all Muslims and Hindus, were told they had to bite off cartridges for their guns that were greased in animal fat.This violated the religious beliefs of the Sepoys, and they were outraged. The initial mutiny grew, and the rebellion spread throughout northern and central India before it was squashed by the British. The rebellion was completely unsuccessful, and British power over India actually increased. British rule lasted until India finally gained independence in 1947.
2 US Events (Chapter 25)
1882 Chinese Exclusion Act

In 1882, the Chinese Exclusion Act was passed by Congress and signed into law by US President Chester Arthur. The act was one of the most significant restrictions ever made on immigration in the US. The Chinese Exclusion Act banned Chinese laborers from immigrating to the US. This immigration act was similar to restrictions made on immigration by countries in Europe at the time. It was one of the "great white walls" that prevented Asians from immigrating to the US and Europe during the age of imperialism.
Annexation of Hawaii

In 1893, the Kingdom of Hawaii was overthrown in a coup led by mostly American citizens living in Hawaii. Queen Liliʻuokalani was arrested, and the Republic of Hawaii was established. Almost immediately after the overthrow, the new government of Hawaii petitioned to be annexed by the US. After a couple of years, annexation was sucessfully negotiated, and the Newlands Resolution passed Congress and was signed by US President William McKinley, creating the Territory of Hawaii. The picture above shows a ceremony celebrating the annexation. By annexing Hawaii, the US was following the example of European countries, that during this period were going into foreign places and taking over.
US Imperialism
Political Cartoon

This cartoon depicts US forces leaving Iraq after taking down Saddam Hussein. The US troops are passing a sign that represents Iraqi anger at the United States's intervention, and asserts that the US troops are "imperialist pigs". The artist clearly was not a fan of the Iraq War, and believes that US motives for intervention were imperialistic, which is not entirely accurate. The US didn't invade Iraq to civilize its people and exploit its natural resources, but as a part of its "war on terror".
Has the US been imperialistic?
The US invasion of Iraq way not have been imperialistic, but there have been times in the past when the US has acted on imperialism, namely in the Spanish American war, the annexation of Hawaii, and in Panama. In these instances, the US acquired territory for its own gain while extending its authority over other territories.
Political Cartoons

This is a cartoon of John Bull, a personification of Britain, taking in an orphaned baby Uganda, poking fun at Britain colonizing Uganda. The artist is showing the condescending and paternalistic attitude of imperialism, showing that the British view the country and people of Uganda as childish, or incompetent.

This cartoon is mocking the idea of the "white man's burden", showing instead the black man's burden, depicting an African man carrying all of the troubles European involvement in Africa wrought.
Introduction: Chapter 25
Chapter 25 is about the age of new imperialism, and western expansion. With the industrial revolution, both Europe's strength and need for natural resources rapidly increased. As Europeans set out to acquire resources and open new markets, they conquered and "civilized" other peoples, leaving very little of the world untouched.
Chapter Objective:
Understand the causes and effects of new imperialism.
Essential Question: What were the three causes of imperialism?
New imperialism was motivated by commerce, civilization, and Christianity. Europeans involved themselves in foreign continents to pursue economic interests and take up the "white man's burden", or civilize and Christianize foreign peoples they saw as inferior savages.
Sunday, February 16, 2014
Self Reflection Chapter 22
There was a lot going on in this chapter. I think I had a decent grasp of everything at the end, but digesting all of the information was a but overwhelming at first. The content seemed to be all over the place. Overall, it was a decent chapter. It wasn't especially exciting, but it wasn't especially dull either.
2 US Events (Chapter 22)
Battle of the Alamo

In 1835, Texas began fighting for its independence from Mexico, beginning the Texas Revolution. The Battle of the Alamo is one of the most famous battles in the fight between Texas and Mexico. Texans were in possession of the Alamo, a former mission, and were attacked and defeated by Mexican forces. But while the Texans lost the battle, they were inspired by their defeat, and went on to successfully fight of Mexico and become the Republic of Texas before being annexed by the United States. Texas, like some nations in Europe during this period, was fighting for its sovereignty.
The Tariff of Abominations

In 1828, the US Congress passed a protective tariff, designed to protect industry in the northern US. Industry in the north was struggling to compete with cheaper, imported goods. The tariff taxed imported goods, eliminating some of the north's competition, and forcing southerners to pay higher prices for their manufactured goods. Naturally, southerners despised the tariff, and dubbed in the Tariff of Abominations. The Tariff of Abominations was similar to the Corn Laws passed in Britain. Both limited the role certain imported goods could play in the economies of their respective nations, and both faced a fair amount of backlash,
Picturing the Past
Liberty Leading the People by Eugene Delacroix
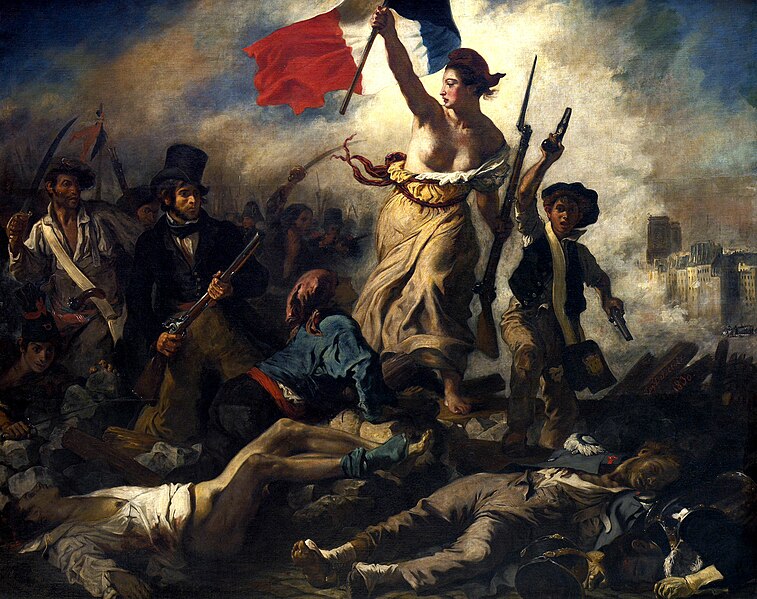

Eugene Delacroix was one of the greatest Romantic painters. He was well known for his dramatic, emotional, and colorful scenes, but he was also known to be a passionate advocate for freedom. In Liberty Leading the People, he paints a powerful picture of the 1830 revolution in France.
Self Reflection Chapter 21
This wasn't an especially interesting chapter. Learning about water frames, steam engines, and the beginnings of the railroad wasn't particularly exciting. A lot of the information we covered seems important, and I'm happy that I now understand it, but we didn't cover anything that I could be enthusiastic about. Digesting information about organizations of industrial workers and different tariffs and labor laws gets to be a bit dull. It's interesting, though, that different inventions and technologies can have such a great impact on the economy. Different industries are constantly changing due to advances in technology. The spinning jenny and steam engine revolutionized industry in the late eighteenth century, and today changes in technology are still constantly altering different industries.
Significant People Chapter 21
Richard Arkwright

Richard Arkwright was an English entrepreneur during the Industrial Revolution. He is credited with inventing the water frame, which was a machine that spun fibers into thread or yarn using water power. Before Arkwright's invention, yarn was made by hand using a spinning wheel. Due to Arkwright's invention of the water frame, the manufacturing of yarn moved from the cottage to the factory, and was able to occur on a much larger scale.
James Watt

James Watt was a Scottish inventor and mechanical engineer during the industrial revolution. Watt made significant improvements on the steam engine that had been developed by Thomas Newcomen. He was able to make Newcomen's engine much more efficient, and went on to make the steam engine a practical and commercial success. The improved steam engine was the greatest advance in technology during the industrial revolution.
Thomas Malthus

Thomas Malthus was an English economist during the industrial revolution. He examined the dynamics of population, and argued that populations would always grow faster than their food supplies. Malthus's dismal assessment was eventually proven wrong, but during his lifetime, his view was generally accepted.
Introduction: Chapter 21
Chapter 21 is about the era of industrialization that occurred in Europe from 1750 to 1850. The industrial revolution led to profound change in European society. The industrial revolution began in Britain, and solidified Britain's status as a dominant world power. During this period industrial workers emerged as a political force, organizing and advocating for political change, and new attitudes emerged on child labor.
Chapter Objective:
Understand the causes and effects of the industrial revolution.Essential Question: Why did the industrial revolution begin in Britain?
The industrial revolution was able to begin in Britain because of the nation's wealth of natural resources, many harbors, abundance of cheap labor, and its colonial system.
2 US Events (Chapter 21)
The Boston Tea Party

In Boston, on December 16, 1773, the Sons of Liberty, a group of protesters, destroyed a supply of tea that had been shipped to Boston. They were protesting the Townshend Acts, a series of acts that the British parliament had passed instituting various taxes on the American colonies. Part of why the industrial revolution began in Britain was because of Britain's colonial empire; factories in Britain would manufacture goods and then sell them in the colonies with little competition. Though this system satisfied the British and helped to spur the industrial revolution, it wasn't always appreciated in the colonies, leading to events like the Boston Tea Party and, eventually, the American Revolution.
The Invention of the Cotton Gin

In October 28, 1793, an American inventor, Eli Whitney, applied for a patent on the cotton gin he had invented. His machine quickly separated cotton fibers from their seeds. Prior to Eli Whitney's invention, this was done by hand, and took much more time. Just as many different inventions played a role in the industrial revolution in Europe, Whitney's invention revolutionized the cotton industry in the US. The cotton gin greatly increased the productivity of cotton farms. However, the cotton gin also led to the growth of slavery in the US.
Significant People Chapter 22
Count Henri de Saint-Simon

Saint-Simon was a French socialist. He was one of the most influential early socialist thinkers, and believed that every social institution should have improving the conditions of the poor as its greatest priority. Saint-Simon also believed society was comprised of "doers" and "parasites", and that the "doers" should be in control and carefully plan the economy.
Pierre Joseph Proudhon

Pierre Joseph Proudhon was a French socialist and anarchist. Proudhon believed that property was theft, or profit that was stolen from the worker, and proclaimed this idea in a pamphlet, What Is Property. He is considered to be the father of anarchism. Proudhon also corresponded with, and influenced, Karl Marx.
William Wordsworth
William Wordsworth was an accomplished English poet and one of the leaders of English romanticism in literature. Together with Samuel Taylor Coleridge, Wordsworth published Lyrcial Ballads, which launched the Romantic movement in English literature.
Introduction: Chapter 22
Chapter 22 is about the dual revolution that occurred in Europe from 1815 to 1850. After 1815, economic and political changes reinforced each other. This period encompassed the birth of the Romantic movement and the emergence of nationalism and French and Marxian socialism. It was a time of immense change and upheaval.
Chapter Objective:
Understand the ideologies and upheavals that occurred from 1815 to 1850.
Essential Question: What were liberalism, nationalism, and socialism?
Liberalism was a movement that focused on liberty and equality, and believed in representative government. Nationalism was the idea that each people had genius and cultural unity, which often led to wishes for an independent political state. Socialism was a movement focused on cooperation and community. Socialist leaders believed in economic planning, economic equality, and state regulation of property.
Listening to the Past
London
I wander thro' each charter'd street,
Near where the charter'd Thames does flow.
And mark in every face I meet
Marks of weakness, marks of woe.
In every cry of every Man,
In every Infants cry of fear,
In every voice: in every ban,
The mind-forg'd manacles I hear
How the Chimney-sweepers cry
Every blackning Church appalls,
And the hapless Soldiers sigh
Runs in blood down Palace walls
But most thro' midnight streets I hear
How the youthful Harlots curse
Blasts the new-born Infants tear
And blights with plagues the Marriage hearse
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)